12 SEO Metrics That Define Your Success 


You’ve optimized your website for keywords. You’ve built up backlinks from authoritative sources, you’re developing high-quality content, and your site is lightning fast and mobile friendly.
You’ve done everything by the book, which means you should be well on your way to climbing the rankings in search engine results pages.
But here’s the question: how do you know if your SEO is ACTUALLY working?
See, SEO is all about playing the long game. But when you’re measuring progress over 3, 6 or even 12 months, it’s tough to discern if your actions are moving the needle. And by the time you do, it can take another few months to course correct any issues or fix any mistakes.
That’s why data is so important.
When you track your SEO performance, you’ll have the knowledge of which tactics are working and which aren’t. More importantly, this data gives you (or your SEO agency) the power to drive refine your SEO to get an even better ROI.
It’s not enough to measure just one metric though. You need big-picture reporting if you want to drive big revenue results. That means focusing on a wide range of metrics, covering engagement, traffic, conversions, ROI metrics and more.
In this post, we’ll look at 12 SEO metrics you should be tracking to achieve success from your SEO efforts. These include:
- Organic traffic
- Click-through rate
- Backlinks and referring domains
- Conversion rate
- Dwell time
- Average time on page
- Bounce rate
- Pages per visit
- Pages indexed
- Page Speed and Core Web Vitals
- Keyword rankings
- ROI
Let’s get started.
What is a KPI in SEO?
A Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is a quantifiable value that can be used to evaluate the success of your SEO efforts. These SEO metrics help measure whether your current strategies are working, how effective they are, and where there’s room for improvement. Some of the most common SEO KPIs include rankings, organic traffic, backlinks, and pages indexed.
If you’re investing in SEO, you should be tracking your performance — otherwise, you’re just flying blind. However, if you’re working with an agency, SEO KPIs are even more important because they’re indicative of whether the agency is hitting its targets and achieving the desired outcomes from your investment.
Top SEO metrics to measure for success
1. Organic traffic
What’s the number one reason businesses want to rank higher on Google?
Simple: to get more organic traffic to their website.
Organic traffic refers to any traffic you get from search engine results pages (SERPs) without paying for an ad. If you see an increase in visitors from organic search, this is a pretty good indicator that your campaign is working and you’re increasing your website’s visibility in organic search results.
Luckily, it’s pretty easy to track your website’s organic traffic volume.
Just log into Google Analytics, then navigate Audience > Overview and select Add Segment:
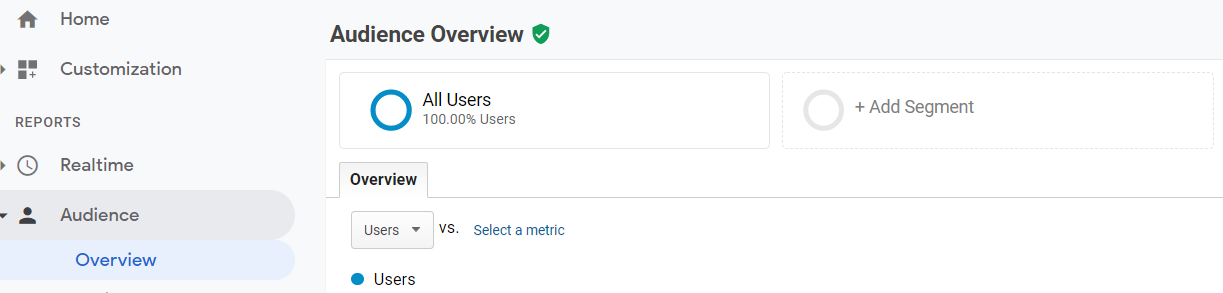
Select organic traffic from the list:
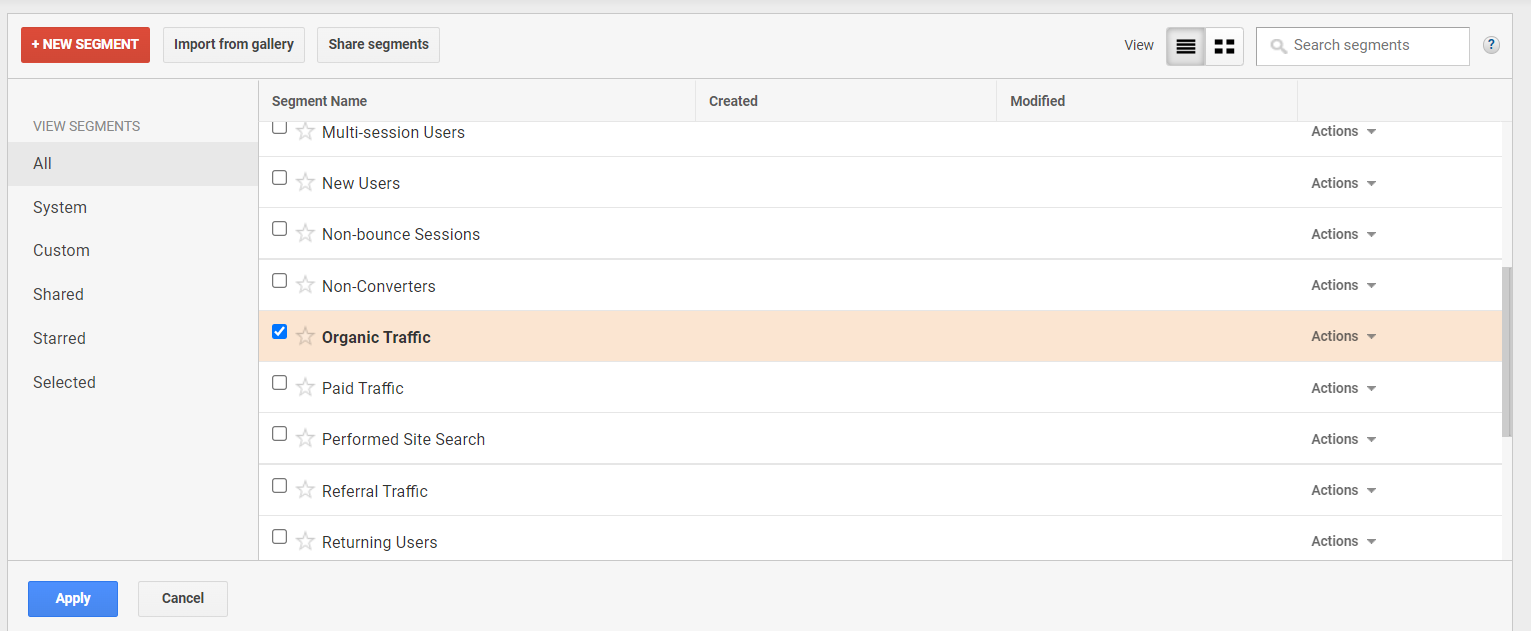
You should then be able to see organic traffic as a total percentage of traffic to your website:
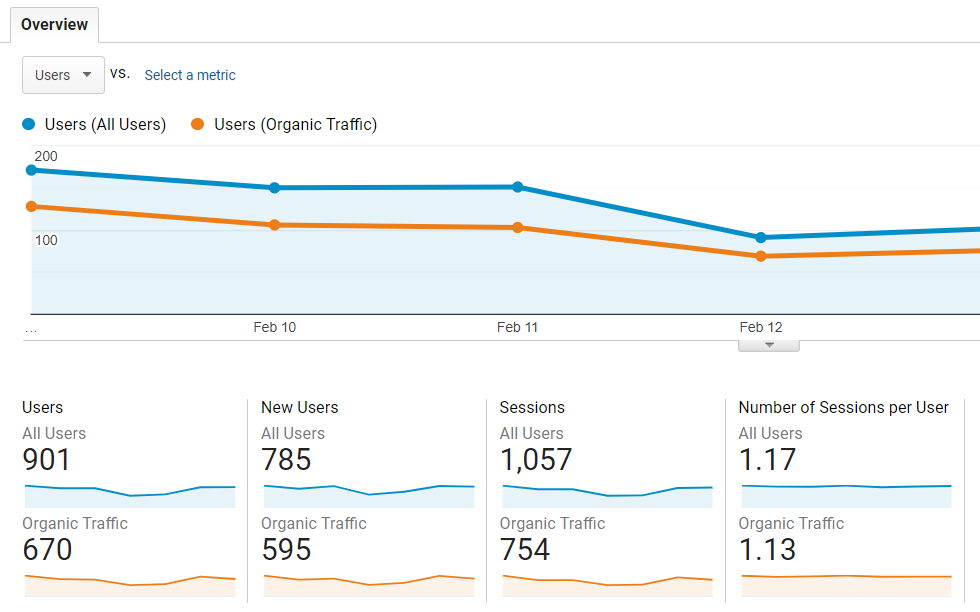
How do I get organic traffic?
Organic traffic comes from unpaid search engine results, such as those on Google or Bing. Every time you show up in organic search results and a user clicks through to your page, that’s counted as one visitor. The more times you appear in search results, the more users click through — and in turn, you’ll get more organic traffic.
This is where SEO comes in.
SEO is the main strategy to increase your organic traffic because it helps you increase your position in SERPs. When you move up just one spot on search engine results, your clickthrough rate can increase as much as 30.8%. As you rank higher, the chances of a user clicking through increase, with the #1 organic result 10x more likely to receive a click than the #10 result.
Why organic traffic is important?
Organic traffic is important to websites because it’s highly targeted. When you rank for a relevant keyword, such as “best gardening tools”. you’re reaching your target audience at the exact moment that they’re looking for your products and services. If you deliver valuable content that addresses their search intent, you can influence their decision-making and build awareness for your brand.
What’s more, unlike PPC platforms like Google Ads, every click you get from organic traffic is absolutely free. So if you want to increase ROI on your marketing dollars, organic traffic is one of the best ways to do it.
What is the difference between organic and direct traffic?
Organic traffic is any traffic that comes through from unpaid listings on SERPs. Direct traffic, on the other hand, measures people who navigated to your website by directly typing your URL into their browser.
If someone searches for “Online Marketing Gurus” and clicks through to the top Google result, that would be counted as organic traffic:
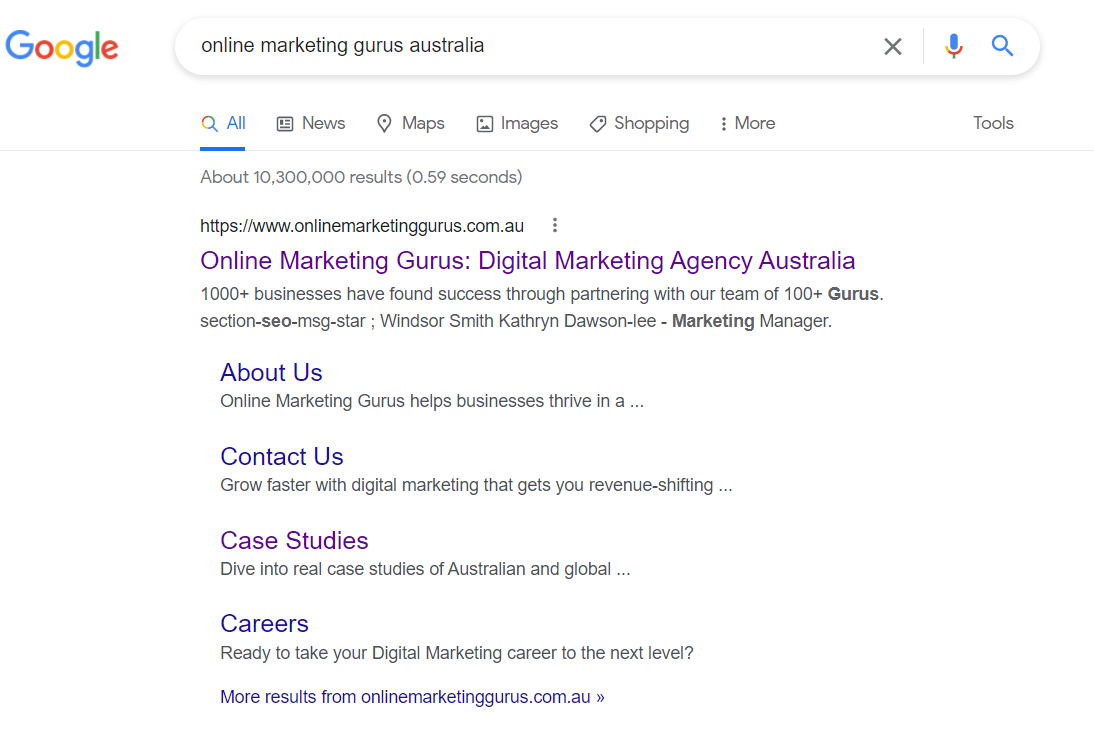
However, if they typed https://www.onlinemarketinggurus.sg/ into their browser, that would be counted as direct traffic:

2. Click-Through Rate (CTR)
Search click-through rate is the percentage of users who clicked through to your page from the organic search results, out of the total number of searchers who saw the search engine results (aka Impressions).
CTR is way more important than your ranking position on Google. What’s the point in ranking high for a keyword if nobody is clicking to your site?
But unless you know the benchmarks, CTR is just another number. You need context to see how you’re tracking.
This graph provides context:
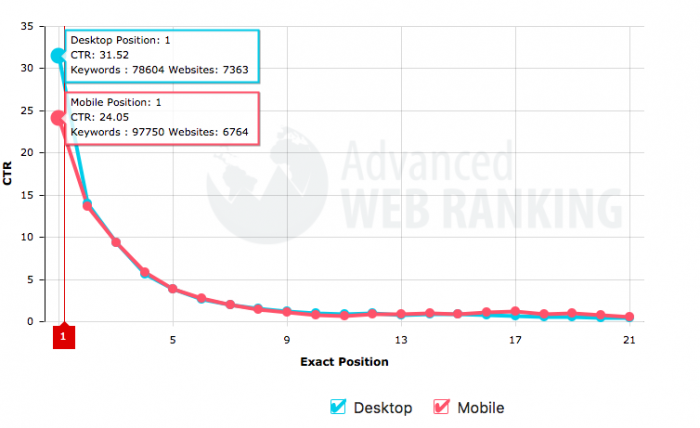
You can see how the top three search results have a huge average CTR. It’s over 30% in first position dropping to 10% in third position.
In other words, the top three positions typically grab the lion’s share of organic search traffic.
After that it drops quickly to just 2% CTR for positions 9 and 10.
Now it’s time to find your CTR.
Go to Google Search Console:
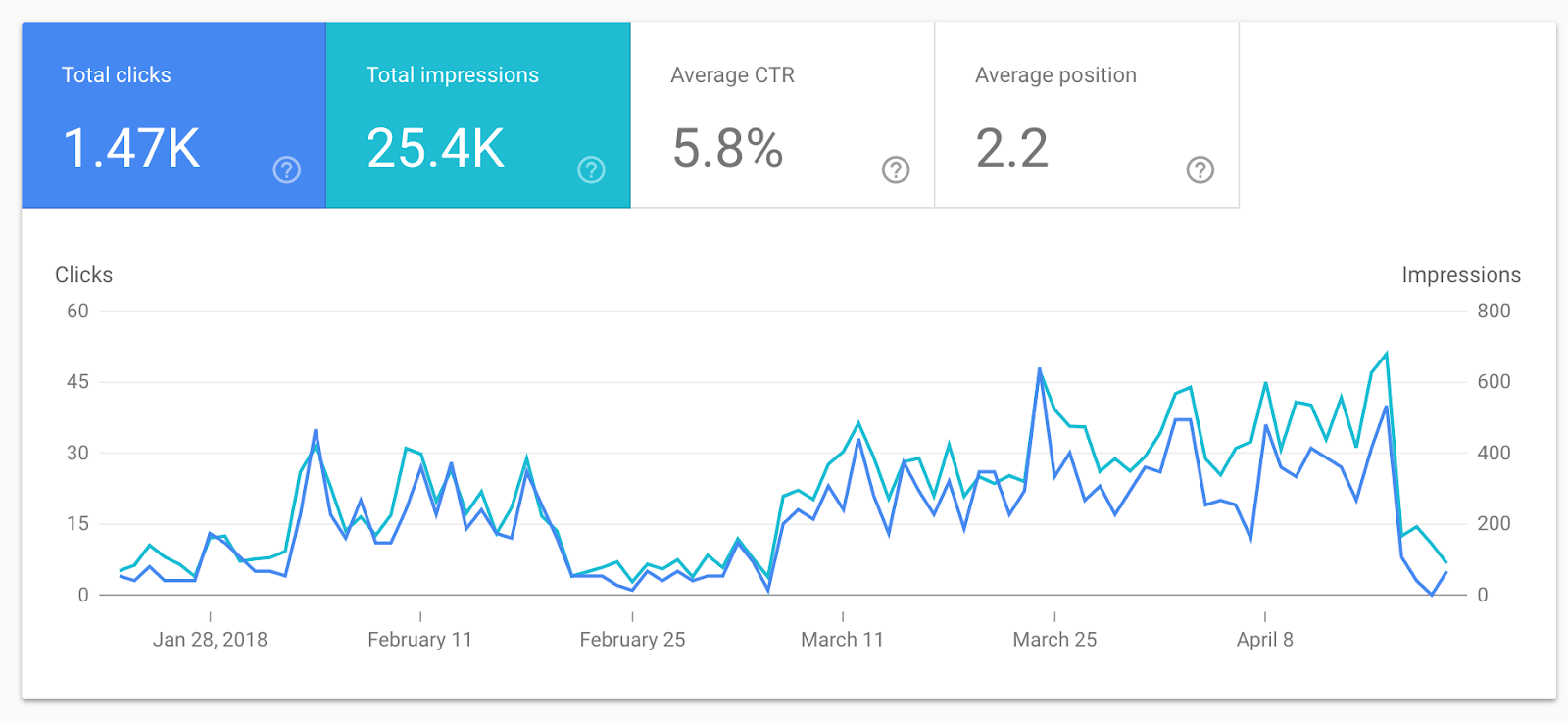
Image credit: Search Engine Journal
It clearly shows you the number of clicks vs impressions, and how this trends over time.
3. Backlinks and referring domains
We know what you’re thinking – why measure links? Surely there are more important SEO metrics to track?
But consider this: you already know how important links are to search engine optimisation. Google uses quality backlinks as a ranking factor to determine whether your site is an authority and useful to searchers. The more high quality, relevant backlinks you have, the more likely you will rank highly in the search results and acquire high domain authority.
So, it makes sense that you need to track links as a metric.
But you can’t just track the number of backlinks.
Google doesn’t rank you based on having a huge volume of links pointing to your site.
You need to track the quality of backlinks.
If you have hundreds of links, you haven’t got time to trawl through every link and see if it’s relevant and high quality.
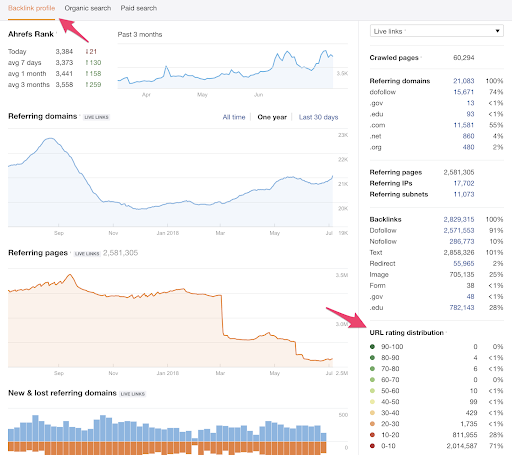
So, use these tools to help:
- Google Search Console
- SEMrush
- Moz’s Link Explorer
- Ahrefs
Ahrefs is particularly useful, as it lets you check the URL rating distribution – the percentage of backlinks that are high quality vs low quality.
4. Conversion rate
Now we’re getting to the really meaty SEO metrics – the SEO metrics you can start using to build your business case for search marketing and refine your SEO strategy for the maximum ROI.
Conversion rate is the percentage of visitors who take a specific action against a goal. The goal is whatever you want it to be for that specific page: email signup, ebook download, a purchase, phone call, and so on.
Knowing your conversion rate starts to give you a clearer idea on the return on investment (ROI) of your SEO efforts.
There are a few practical ways you can put your conversion rate insights to work. For example, you can compare the conversion rates of content to see which pieces are driving more conversions. Then, use this to drive your content strategy in a better direction.
How do track organic conversions?
First, you need to set up goals in Google Analytics.
For an eCommerce site, this is simple – you’ll want to set up goals based on transactions.
Setting up goals for lead-based businesses (that is, not an eCommerce site) is different because there aren’t actual “transactions” that result in dollars being spent on your site. So, think about what actions you want visitors to take on your site. For example, if the goal of a page is to get visitors to fill in a form for an ebook, set that up as a goal.
Then, GA will show you the conversion rate against this goal.
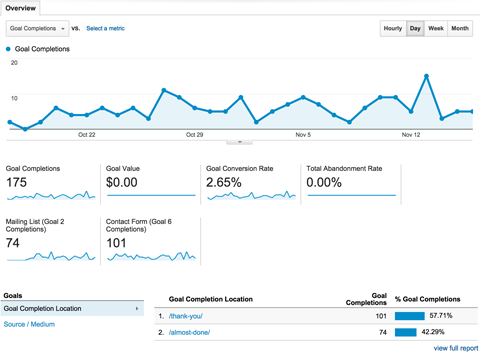
Image Credit: Social Media Examiner
Again, you need context to understand how you are really performing.
What makes a GOOD conversion rate for your site?
Check the average conversion rate for your industry. The data below is a few years old, but it provides a starting point. You can always do some quick research to find your specific industry benchmark.
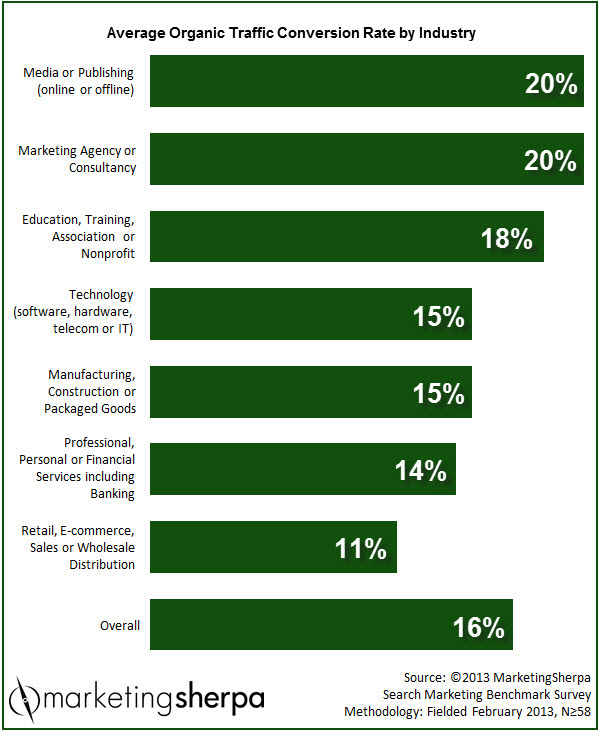
Image credit: Marketing Sherpa
Now, how does your conversion rate stack up against the rest?
If you’re falling behind, it’s time to take action.
5. Dwell time
Dwell time is the length of time a visitor spends looking at a page after they’ve clicked through from search engine results.
It’s considered one of the SEO metrics for engagement, as it can tell you how effective your content is at solving a searcher’s query.
Think about it, the more time you spend consuming the content on a page, the higher the chances that page satisfied your needs.
6. Average time on page
Average time on page is the average amount of time a visitor spends on one of your pages before going anywhere else.
This can be very informative when it comes to your content.
Let’s say you have a 4,000-word blog post that you know takes 12 minutes to read. But visitors are only spending on average 45 seconds on the page. Clearly, the content isn’t hitting the mark.
Maybe the title is misleading, which means people click away pretty quickly. Or the content isn’t high quality enough for people to invest much time in it.
At the same time, a low average time on page isn’t always bad news. People don’t spend much time on the Contact Us page, and if they do it’s probably because you haven’t included the contact information they need.
Go to Google Analytics to find average time on page:
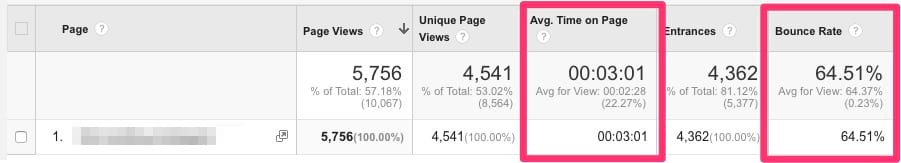
Image credit: Ahrefs
7. Bounce rate
Bounce rate tells you when searchers visit only one page on your site, then return to the search results.
Many SEO experts put a lot of weight on bounce rate for SEO metrics, saying that it influences your organic search ranking.
Research by WordStream even shows a correlation between bounce rate and rankings. The lower the bounce rate, the better the rankings.
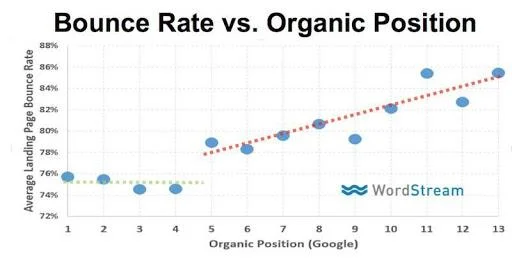
But it’s not that cut and dry.
Bounce rate can be misleading as a measure of SEO success because even if some of the bouncers arrived on your site via a search result, it doesn’t mean they clicked back to Google. Maybe they navigated directly to another site or closed their browser completely.
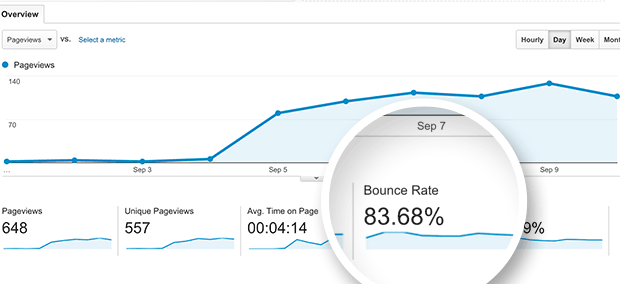
Image Credit: Monster Insight
What is a good bounce rate?
Unfortunately, there is no simple answer for this one as bounce rates vary wildly between industries. The average bounce rate for one industry might be as low as 10%, while another might be as high as 80%. Generally speaking though, a bounce rate between 26% to 40% is good, and a bounce rate between 41% to 55% is average.
If you want to take it one step further, you can still benchmark your bounce rate against your industry average to see where you stack up using these insights from SimilarWeb:
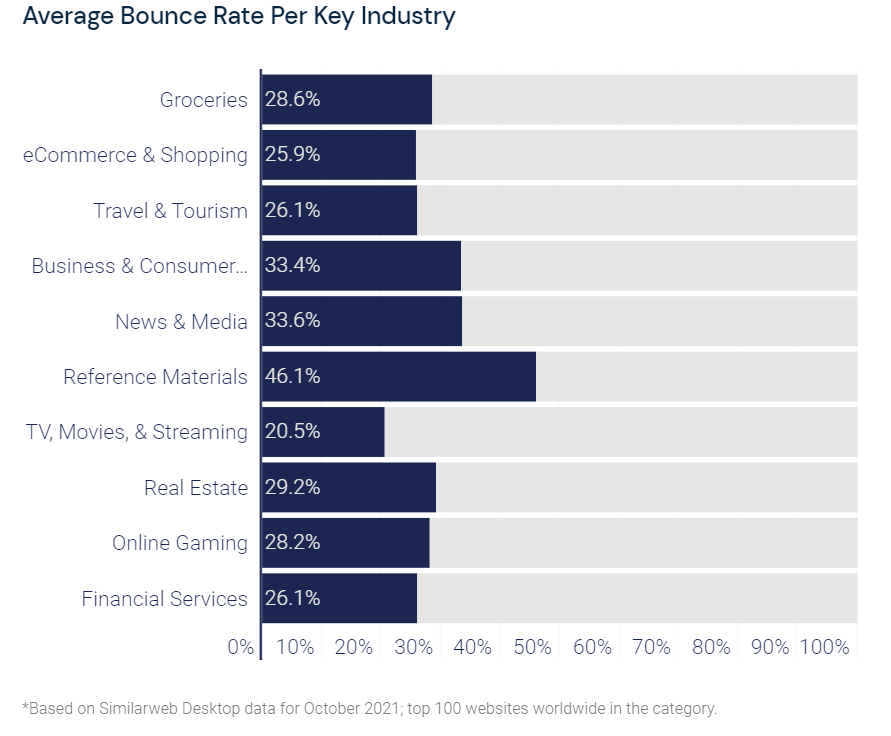
What does a high bounce rate mean?
If your bounce rate is higher than average, this might be a sign that you need to fix something on your website.
A high bounce rate can be caused by a number of factors, but the most common are:
- The content doesn’t match the search intent. If a user lands on your website expecting to see one thing and get something else entirely, they’ll quickly navigate away and look for answers elsewhere.
- A negative user experience. For example, your site may load too slowly or users may be struggling to read and digest your content.
- Visitors don’t have any reason to keep clicking. Let’s say someone clicks through to your website and finds the exact answer to their question FAST. Unless you give them a reason to stay, they’ll just pop onto your page, get the information they need, then go about their daily business.
- Technical errors, such as a 404 error page or a loading error.
Don’t worry though — a high bounce rate can usually be solved by making a few improvements to your website.
How is bounce rate calculated?
Bounce rate is calculated using the following formula:
Bounce rate = Number of single-page sessions / Total website sessions
Let’s say you have 15,000 total website sessions and 5,700 of those are single-page sessions. In this case, your bounce rate would be 5,700/15,000=0.38, or 38%.
Is a low bounce rate good?
Yes, but only to an extent. There are some cases where a low bounce rate can be caused by a duplicate Google Analytics code, or referral and bot spam. These technical issues artificially lower your bounce rate, which means you’re clueless about the TRUE performance of your SEO campaign.
As a rule of thumb, you should investigate any bounce rate that’s lower than 10%, and be mindful of drastic changes in your bounce rate from one month to the next.
8. Pages per visit
Sometimes the goal of your web page is to convert visitors instantly. You want them to fill in a form, submit a query or purchase right there and then.
Other times, the goal is to keep visitors engaged and lead them through to other pages, which take them even deeper into the sales funnel. This is especially valuable for eCommerce and service-based businesses.
The more pages people browse on your site, the more likely they are to buy something.
This is where pages per visit can be a helpful metric.
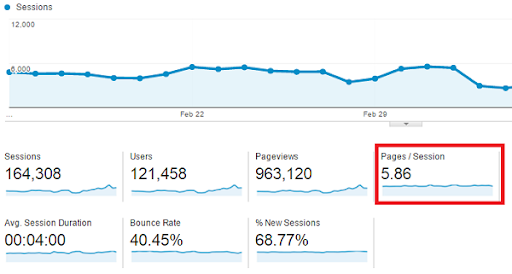
Source: Google Analytics
Along with bounce rate and average time on page, pages per visit is an engagement metric that plays an increasingly important part in determining your search ranking.
The more time users spend on your site, the more they like your content, or so the theory goes.
Of course, it could also mean visitors aren’t finding what they need – but that’s where you need to look at other important SEO metrics to see the whole picture.
9. Pages indexed
Index status is usually overlooked as an SEO measure, but it can be incredibly handy in telling you how your site is performing with search bots and crawlers.
Go to Google Search Console and navigate to Google Index > Index Status.
This tells you which URLs the Googlebot has tried to index.
You should see something like this:
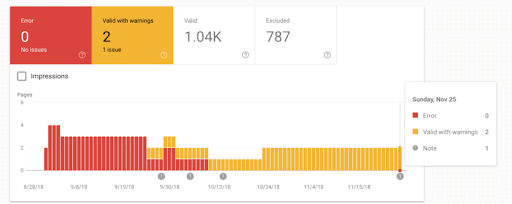
(Image credit: SearchEngineLand)
Use it to identify any issues which could be preventing your pages from showing up in the SERPs.
Notice any sudden drops or sharp increases in indexed pages? Look into them.
10. Page Speed and Core Web Vitals
Page speed and Core Web Vitals are both massive contributors to the success of your SEO campaigns. These SEO metrics are linked to your site health and the overall user experience that you deliver to your site visitors.
Let’s start with the first one: Core Web Vitals.
What are the Core Web Vitals?
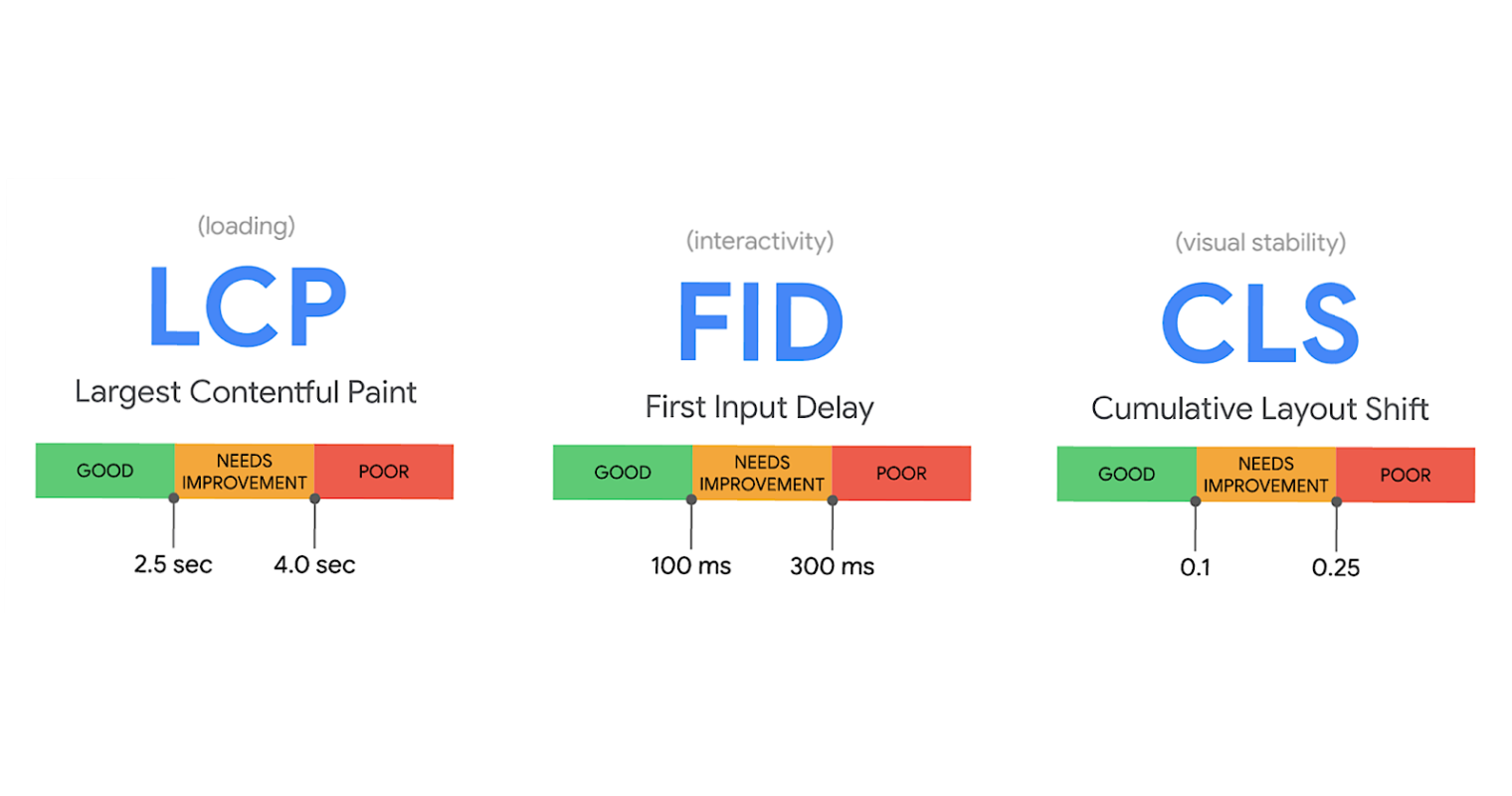
Core Web Vitals are a new set of performance metrics that measure how users experience the speed, responsiveness, and visual stability of your website. These are important because they’ve been key ranking factors for Google’s search algorithm since May 2021 — and ignoring these could cause your website to be downranked in SERPs.
There are three key SEO metrics that make up Core Web Vitals:
- LCP, or largest contentful paint. This is the amount of time it takes for your website’s primary content to load.
- FID, or first input delay. This metric measures how long it takes for a page to be fully interactive for users.
- CLS, or cumulative layout shift. CLS refers to any unexpected layout shifts on a website’s visual content, such as an image that randomly changes its size or a video that disappears as users scroll.
How to find your Core Web Vitals
Go into Google Search Console and navigate to Enhancements > Core Web Vitals Report. This report will show you how each of your website URLs are performing based on their status, metric, and even by groups of similar web pages.
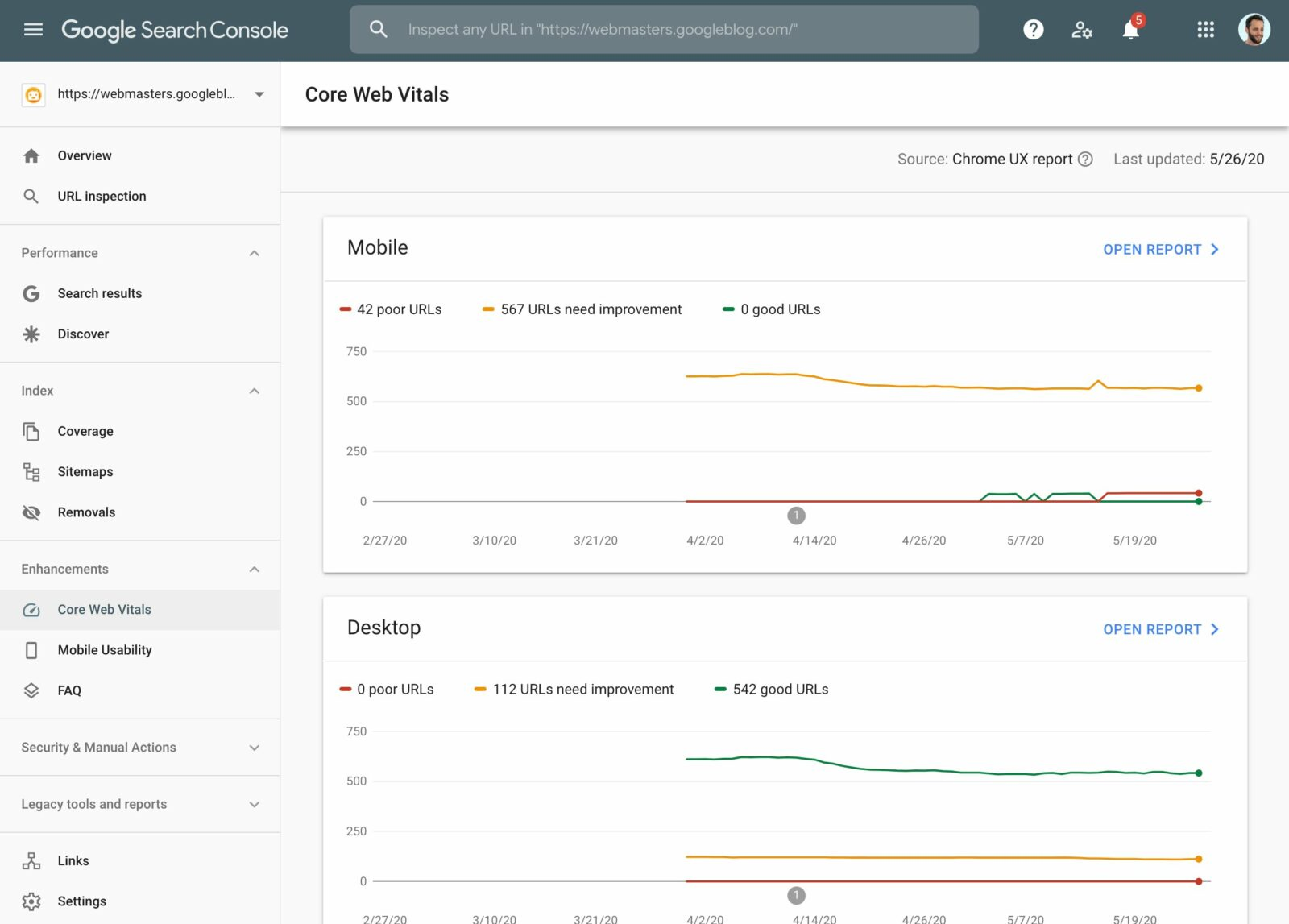
Within this report, you can see which URLs are underperforming, which need improvement, and which are good. Prioritise the “Poor” URLs first, then tackle the “Needs Improvement” ones.
Why is page speed important?
Page speed is important because it’s a critical ranking factor for search engines — and a critical component of delivering an outstanding user experience.
Need more proof? According to Portent, a website’s conversion rates drop by 4.42% on average with every additional second of load time between 0 and 5 seconds. Another study by Unbounce found that almost 7 in 10 consumers say an eCommerce website’s loading speed impacts their willingness to shop from that retailer.
Google likes websites that load fast, and so do customers. So if you want to improve your rankings and increase conversions, you NEED to be optimizing your page speed.
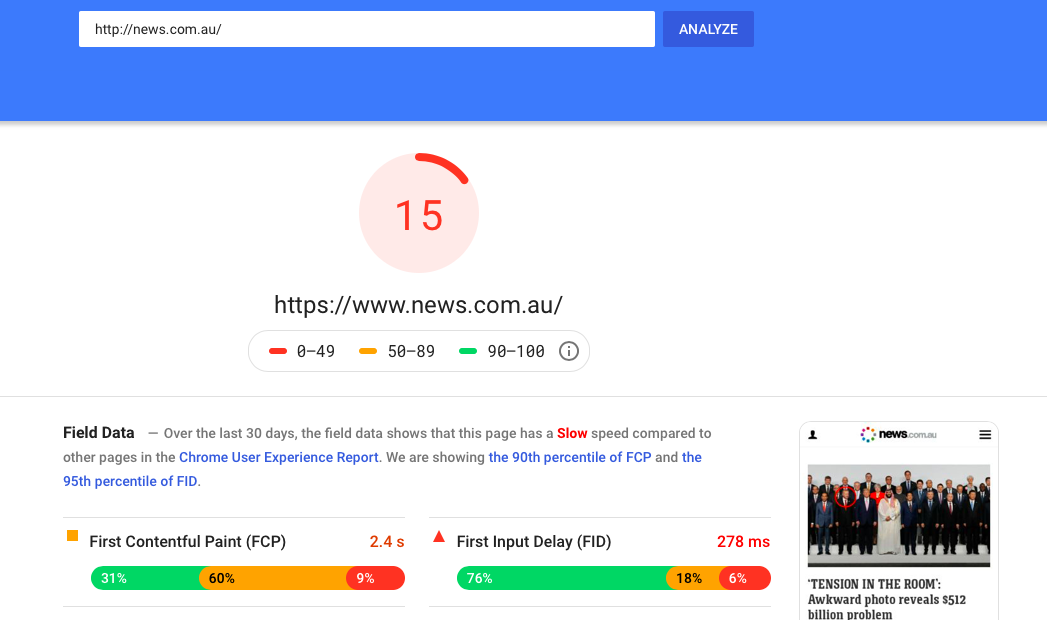
How to find your site speed
To see your site speed, go to Google’s PageSpeed Insights and type in your page URL.
Your page load time is an important ranking factor for Google but also impacts your user experience and conversion rates.
Soon this data will be available within Google Search Console, making it even easier to track and see possible problems.
11. Keyword Rankings
We had to include keyword rankings on the list of important SEO KPIs. But you need to look beyond simply which ranking position your website is at.
How are organic rankings tracking over time? Are they dropping or lifting with different trends and seasons? Which keywords bring in the most traffic (highest CTR)?
What does rank mean in SEO?
Your rank in SEO refers to the position that your website appears in SERPs. A page’s ranking is influenced by a number of factors, including content relevance, page authority, on-page SEO, CTR, and more.
You’ll rank differently for specific search terms, which is why it’s important to track your keyword rankings for the individual search terms that you’re targeting, as well as your overall website ranking.
How do I find my keyword rankings?
Go to Google Analytics and track performance over time for Search Visibility, Search queries, Average Position and Traffic.
In Google Analytics, you should see something like this:
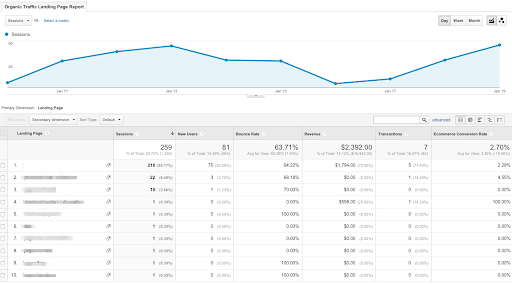
Image credit: Shopify
You can also track keyword rankings using Google Search Console. Track which of your web landing pages are ranking on the first page of Google for their target keywords.
Go to your Google Search Console dashboard, click on “Search Traffic” and then “Search Analytics”.
You should see something like this:

If certain keywords haven’t been doing as well (aka your keyword rankings are low) this is where you can identify them and work out how to tackle them.
Need a benchmark?
See how your keyword rankings against your main competitors.
Use SEMrush to help.
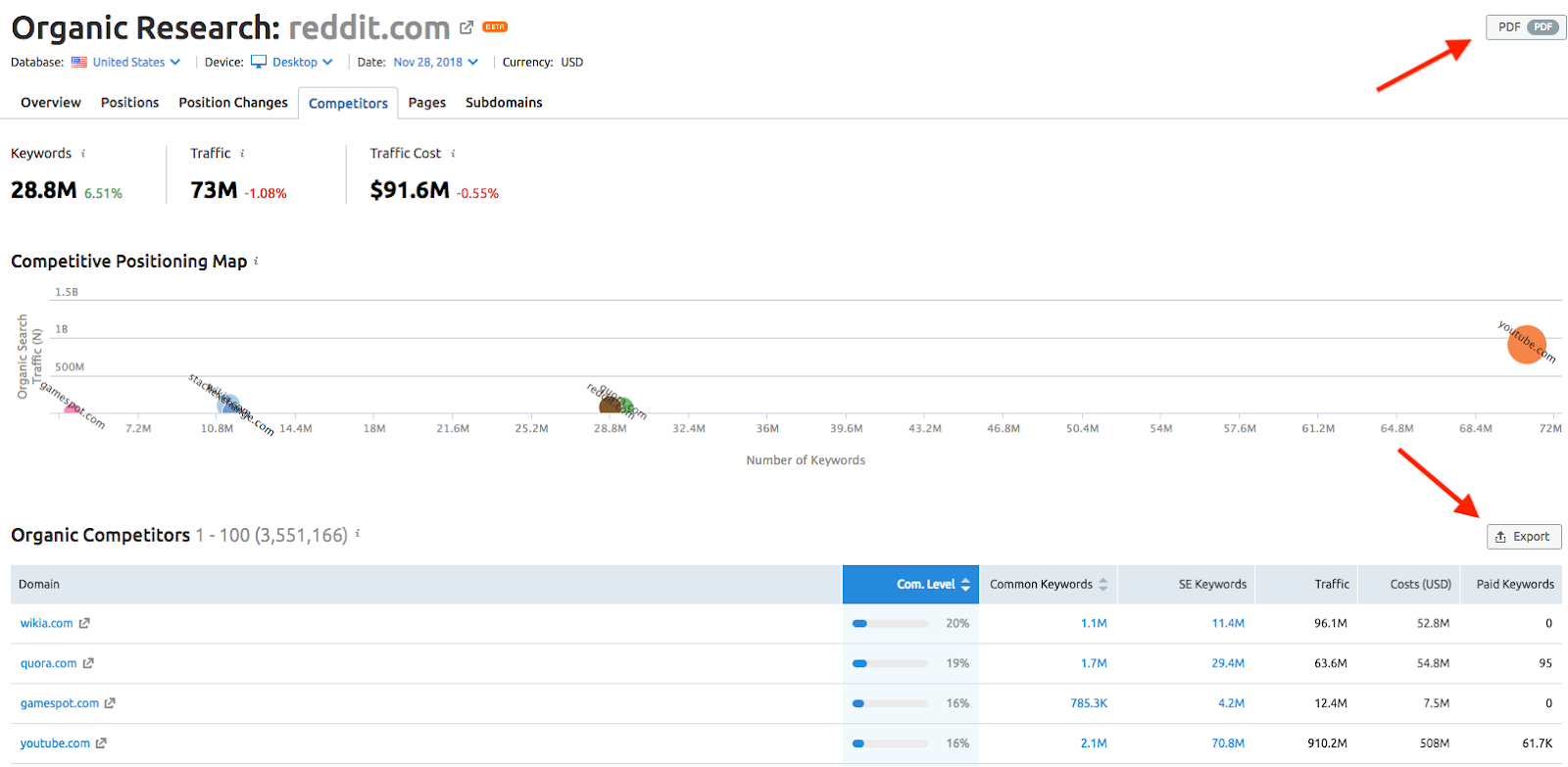
12. ROI
This is where you bring everything together and link it back to your business goals. Are you achieving actual sales, conversions and revenue from SEO? How is this improving over time? Where are the opportunities to do better?
Use your conversion rate and goal tracking here.
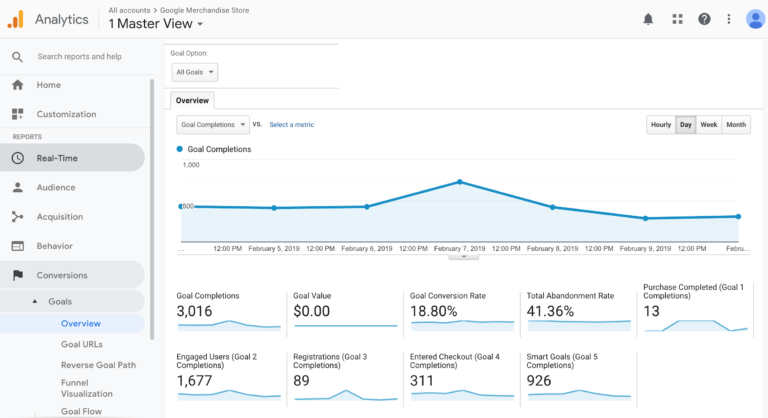
Image Credit: Search Engine Journal
Run a conversion report through GA to see the number of conversions and the value of these conversions. In other words, how much revenue has been generated? Have you met your SEO KPI?
Now, to work out the return on investment, simply compare these values with the amount of money spent on your SEO campaign over the same period.
Granted, it’s not an exact science, but you’ll get a good idea of how your SEO campaigns are impacting on business objectives.
Expect your SEO ROI to change from month to month. You will likely start with a negative ROI in the beginning, where you spend more to set up campaigns and optimize your website. But that’s common – especially when you consider the SEO results time-frame. It’ll be a few months into your campaign where you’ll really start seeing the growth. And after 8-12 months, your ROI will be showing some incredible results.
Do the same with your other digital marketing channels – calculate the ROI of your PPC advertising, social media advertising and email marketing.
But don’t just pour all your budget into the channel that’s performing the best. It might be that PPC is performing especially well because SEO is contributing to a strong brand awareness. That doesn’t mean you should pull all your investment from SEO. Remember that digital channels work better together.
Over to you
Tracking these important SEO KPI’s is an absolute fundamental of any SEO campaign. Relying on guesstimates never works for long in any digital marketing strategy, and especially not SEO.
Knowledge is power. Start tracking from the start and you’ll have the power to refine and improve your SEO campaign to see some real revenue results. Want to find out how to build the foundations of a revenue-busting strategy? Get your free Ultimate SEO Guide to increase traffic and skyrocket your rankings!